Introduction
Welcome, muscle builders and fitness aficionados! Ever ponder the intricate details behind bulking up? It’s not merely about heaving weights and hoping for the best. Delving into the “Muscle Growth Science” unveils a world where exercise meets biology, creating a roadmap for monumental gains. This guide is your ticket to understanding the complexities of muscle development, setting the stage for smarter, more efficient workouts tailored to your body’s unique needs.
Building muscle is a nuanced symphony of biological processes, nutritional finesse, and tailored exercise regimens. By unlocking the scientific principles underpinning muscle hypertrophy, you’re not just lifting weights; you’re architecting your physique with precision and insight. Ready to elevate your muscle-building game? Let’s unravel the science behind muscle growth, empowering you with the knowledge to sculpt your body like never before.
Fundamentals of Muscle Growth
Muscle hypertrophy, the cornerstone of muscle growth, is a fascinating process rooted in our body’s response to resistance training. But what ignites this transformative journey from regular Joe to muscle-bound hero? It begins with understanding the fundamental building blocks of our muscles and how they adapt and enlarge through specific stimuli.
The Role of Muscle Fibers and Satellite Cells
At the muscular level, our bodies are equipped with two main types of fibers: type I (slow-twitch) and type II (fast-twitch). Type I fibers excel in endurance, powering long-duration activities, whereas type II fibers dominate in strength and power, coming into play during short, intense bursts of activity. Muscle growth predominantly occurs in type II fibers, expanding in size through rigorous training and proper nutrition.
Satellite cells also play a pivotal role in muscle development. Think of these cells as the repair crew, springing into action post-workout to mend the microtears caused by lifting weights. This repair process, coupled with the accumulation of more protein within muscle cells, is what leads to muscle hypertrophy. Understanding these “Hypertrophy mechanisms” is crucial for anyone looking to maximize their muscle growth potential.
Progressive Overload: The Trigger for Growth
A key principle in muscle development is progressive overload, which involves gradually increasing the weight, frequency, or intensity of your workouts. This continuous challenge is what signals your muscles to grow in strength and size, adapting to the ever-increasing demands being placed on them. Mastering the “Science of progressive overload” ensures that your muscles are constantly being pushed to their limits, fostering an environment ripe for growth.
Protein Synthesis and Muscle Development
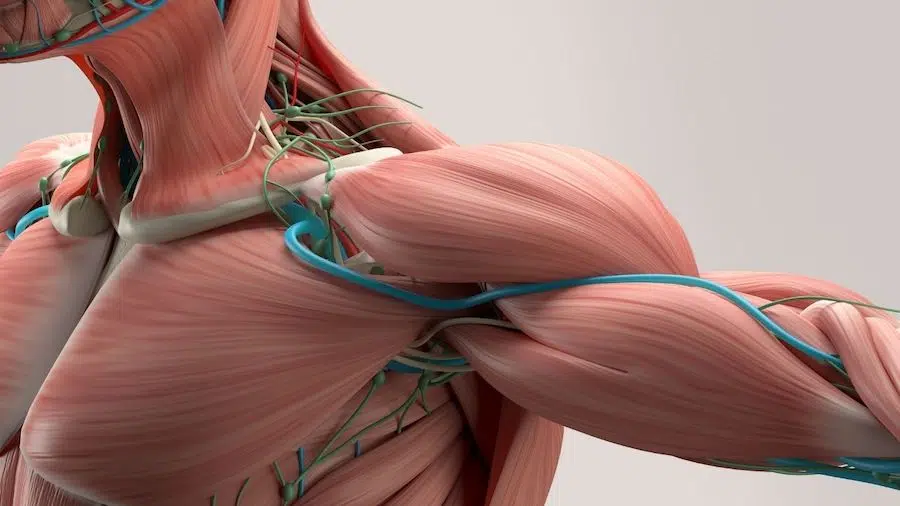
Muscle protein synthesis is the driving force behind adaptive responses to exercise.
Muscle growth is intrinsically linked to the body’s ability to synthesize protein. After all, muscles are made of protein, and without it, they simply can’t grow. But how does one optimize this process to ensure maximum gains? The answer lies in understanding the delicate balance of muscle protein synthesis and breakdown.
Fueling Muscle Repair and Growth
Following a workout, your muscles are primed for repair and growth, a process heavily reliant on protein synthesis. This is your body’s way of rebuilding the muscle fibers that were stressed during exercise. To fuel this reconstruction, a steady supply of protein is essential. Research suggests aiming for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily, though individual needs can vary based on training intensity and overall diet.
The Timing and Quality of Protein Intake
It’s not just about the quantity of protein, but also its timing and quality. Consuming high-quality protein sources—rich in essential amino acids—shortly after your workout can significantly enhance the muscle repair process. This strategic timing, often referred to as the “anabolic window,” is believed to maximize the body’s ability to utilize protein for muscle repair and growth.
Incorporating a variety of protein sources throughout the day also ensures a constant supply of amino acids to your muscles, supporting ongoing protein synthesis. By understanding and applying these principles of “Optimizing protein synthesis for muscle development,” you can create an optimal environment for muscle growth, turning your hard work in the gym into visible, tangible gains.
Hormones’ Role in Muscle Growth
When it comes to “Muscle Growth Science,” hormones are the unsung heroes working behind the scenes. These powerful chemical messengers play pivotal roles in facilitating muscle growth, influencing everything from protein synthesis to fat distribution. Let’s dive into the key hormones involved in this process and how they contribute to your muscle-building efforts.
Testosterone: The Anabolic Giant
Testosterone, often hailed as the king of muscle-building hormones, significantly impacts muscle hypertrophy. This anabolic hormone increases protein synthesis, promoting muscle repair and growth. Higher levels of testosterone are associated with increased muscle mass and reduced body fat.
Growth Hormone: The Recovery Booster
Growth hormone (GH), released by the pituitary gland, plays a crucial role in cell growth and regeneration. GH helps stimulate collagen synthesis in skeletal muscles and tendons, aiding in injury recovery and ensuring that your muscles have the support they need to grow.
Insulin: The Nutrient Shuttle
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, acts as a nutrient shuttle, helping to transport glucose and amino acids into muscle cells. This process is essential for energy production and the synthesis of new muscle tissue, making insulin a critical player in post-workout recovery and growth.
Understanding how these hormones influence “Muscle growth science” can help you tailor your diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices to optimize your body’s hormone production for muscle growth.
Progressive Overload: Scientific Approach
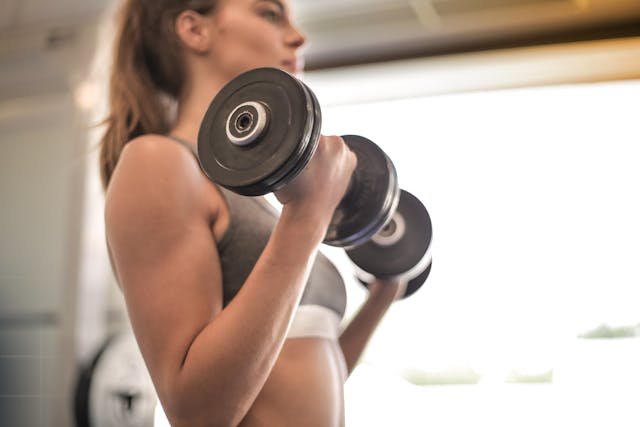

Progressive overload improves overall performance allowing athletes to keep increasing the intensity of their training sessions.
Progressive overload is a fundamental principle in the science of muscle growth. It refers to the practice of gradually increasing the weight, frequency, or intensity of your workouts to challenge your muscles continually. This method is crucial for inducing muscle hypertrophy, as it forces your muscles to adapt to ever-increasing demands, leading to growth and strength gains.
Implementing Progressive Overload
To effectively apply “The science of progressive overload and muscle adaptation,” consider the following strategies:
- Increase Weight: Regularly add more weight to your exercises to challenge your muscles.
- Adjust Repetitions: Varying your rep range can stimulate different muscle fibers and promote growth.
- Modify Exercise Tempo: Changing the speed of your repetitions can increase muscle tension, a key factor in hypertrophy.
- Alter Rest Periods: Shortening or lengthening rest periods between sets can impact muscle recovery and growth differently.
Implementing these techniques ensures continuous muscle adaptation and growth, keeping your workouts challenging and effective.
Nutritional Strategies for Muscle Hypertrophy
Nutrition is just as important as lifting weights when it comes to building muscle. The right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients can significantly impact your body’s ability to grow and repair muscle tissue. Let’s explore the essential nutritional factors influencing “Muscle hypertrophy mechanisms.”
Macronutrient Balance
| Nutrient | Role in Muscle Growth | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Builds and repairs muscle tissue | 1.6 to 2.2g per kg of body weight daily |
| Carbohydrates | Fuels workouts and aids in recovery | 3 to 7g per kg of body weight daily, depending on activity level |
| Fats | Supports hormone production and overall health | 20-35% of total daily calories |
Micronutrients and Hydration
While macronutrients get most of the spotlight, micronutrients and hydration play crucial roles in muscle development and overall health. Vitamins and minerals like Vitamin D, magnesium, and zinc support hormone function and muscle contraction, while adequate water intake ensures optimal cellular hydration and function.
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in “Nutrition for muscle development” alongside a well-planned training regimen is key to unlocking your muscle growth potential. By focusing on both the quantity and quality of your nutrient intake, you can create the perfect environment for muscle hypertrophy, recovery, and overall performance enhancement.
Genetic Factors in Muscle Growth
The role of genetics in “Muscle growth science” is both fascinating and crucial. It’s the genetic lottery that dictates aspects of our physique and capabilities, influencing everything from muscle fiber composition to hormonal levels. Let’s delve into how genetics can shape our muscle-building journey and what it means for individuals with varying genetic predispositions.
Understanding Muscle Fiber Types
Muscle fibers are categorized into two main types: Type I (slow-twitch) fibers, known for endurance, and Type II (fast-twitch) fibers, associated with strength and power. Your genetic makeup determines your fiber type ratio, influencing your potential for muscle growth and how you might respond to different types of training.
| Fiber Type | Characteristics | Impact on Muscle Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Endurance-oriented, fatigue-resistant | Better suited for endurance activities, less pronounced hypertrophy response |
| Type II | Power-oriented, quick to fatigue | Greater potential for size and strength gains |
The Role of Myostatin
Another genetic factor is myostatin, a protein that limits muscle growth. Variations in myostatin-related genes can significantly impact one’s muscle mass potential. Individuals with lower myostatin levels naturally have a higher capacity for muscle growth.
Understanding your genetic blueprint can help tailor your training and expectations. While genetics set certain limits, they don’t dictate your destiny. With the right training and nutrition, you can maximize your genetic potential for muscle development.
The Significance of Recovery and Rest

“Recovery and rest” are not just downtime; they’re integral to the muscle-building process. The science of muscle growth emphasizes not only the work you put in at the gym but also the importance of allowing your body to repair and strengthen itself afterward.
The Physiology of Recovery
During rest periods, the body undergoes critical processes that contribute to muscle hypertrophy. This includes the repair of microtrauma (tiny tears in muscle fibers) caused by intense exercise, replenishment of energy stores, and reduction of inflammation. Neglecting proper recovery can lead to overtraining syndrome, impairing muscle growth and overall health.
| Aspect | Importance in Muscle Growth |
|---|---|
| Sleep | Facilitates growth hormone release, critical for muscle repair and growth |
| Nutrition | Provides the building blocks for muscle repair |
| Active Recovery | Enhances circulation, aiding in nutrient delivery and waste removal |
Adopting a holistic approach to recovery, including adequate sleep, nutrition tailored to repair, and light activities on rest days, can significantly enhance your muscle growth outcomes.
Age and Muscle Regeneration
Age plays a significant role in “Muscle regeneration and growth,” with the body’s ability to build and repair muscle changing as we grow older. Understanding these shifts is crucial for adapting training and nutrition strategies across different life stages.
Age-Related Changes in Muscle Growth
As we age, factors like decreased hormone levels, reduced muscle fiber number, and slower protein synthesis contribute to a decline in muscle regrowth capacity. However, this doesn’t mean muscle growth stops entirely; it signifies the need for adjusted expectations and methodologies.
| Age Group | Considerations for Muscle Growth |
|---|---|
| Youth | Rapid growth and recovery, high adaptability to resistance training |
| Middle Age | Slower recovery, importance of consistency and recovery focus |
| Older Adults | Maintenance of muscle mass critical, emphasis on resistance and balance training |
Adapting training intensity, volume, and recovery strategies according to age can help mitigate the impact of aging on muscle growth, allowing individuals to maintain strength and muscle mass well into later life.
By understanding and applying the principles of genetics, recovery, and the effects of aging on muscle growth, individuals can tailor their approach to muscle development, optimizing their routines for maximum effectiveness across different stages of their fitness journey.
Microtrauma and Muscle Repair
Microtrauma, the small tears in muscle fibers caused by intense physical activity, is a fundamental concept in “Muscle Growth Science.” These tiny injuries are the catalysts for muscle repair and growth, a process known as hypertrophy. Understanding how to effectively manage and optimize recovery from microtrauma is crucial for anyone looking to increase their muscle mass and strength.
The Role of Microtrauma in Hypertrophy
When muscles are subjected to stress beyond what they’re accustomed to—think lifting heavier weights or increasing the intensity of your workouts—microtrauma occurs. This damage signals the body to begin the repair process, which not only heals the tears but also adds additional muscle fibers to prevent future damage, resulting in muscle growth.
| Training Type | Microtrauma Impact | Recovery Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Training | High | Adequate nutrition and rest for repair |
| Endurance Training | Moderate | Less intense recovery, focus on hydration and nutrient replenishment |
| High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) | Variable | Dependent on workout intensity; requires balanced recovery |
Optimizing Recovery for Muscle Growth
To maximize muscle repair and growth following microtrauma, several strategies can be employed:
- Nutrition: Consuming a diet rich in protein and amino acids is essential for repairing muscle tissue.
- Rest: Allowing adequate time for muscles to heal is crucial, highlighting the importance of rest days in any training regimen.
- Supplementation: Certain supplements, like BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids), can support muscle recovery.
Metabolic Pathways and Muscle Development
Muscle development is intricately linked to the body’s metabolic pathways. These pathways provide the energy required for muscle contraction during workouts and play a significant role in the repair and growth of muscle tissue post-exercise. Understanding the interaction between metabolism and muscle development can offer insights into optimizing workouts for maximum gains.
Key Metabolic Pathways in Muscle Development
The two primary metabolic pathways involved in muscle development are the anaerobic (without oxygen) and aerobic (with oxygen) pathways. The anaerobic pathway is crucial for short, high-intensity activities and relies on glucose for energy, leading to the production of lactic acid. In contrast, the aerobic pathway supports longer, lower-intensity activities, using oxygen to convert carbohydrates, fats, and sometimes proteins into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of cells.
| Pathway | Role in Muscle Development | Energy Source |
|---|---|---|
| Anaerobic | Supports muscle strength and size gains | Glucose |
| Aerobic | Aids in muscle endurance and recovery | Carbohydrates, Fats |
Enhancing Metabolic Efficiency for Muscle Growth
To enhance your body’s metabolic efficiency for better muscle growth, consider the following:
- Varied Training: Incorporating both anaerobic and aerobic exercises can optimize energy utilization and muscle adaptation.
- Nutrient Timing: Consuming the right nutrients before and after workouts can fuel the metabolic pathways more effectively. Thus supporting muscle repair and growth.
Conclusion
Unlocking the full potential of muscle growth isn’t just about pushing weights. It is about applying the principles of science to understand and work with your body. From the intricate dance of hormones and genetics to the meticulous balance of nutrition and recovery, every aspect of “Muscle Growth Science” plays a crucial role in achieving your fitness goals.
Now, armed with a deeper understanding of what drives muscle growth, you’re not just working out; you’re crafting a masterpiece. Remember, the journey to muscle growth is a marathon, not a sprint. Stay curious, stay dedicated, and let science be your guide to unlocking your body’s full potential.








